Other Products Available
Roller-Pinion System Comparison
Roller-Pinion Systems (RPS) are a relatively new linear motion product out on the market that claims to surpass the performance of traditional rack & pinion drives. They consist of drive "pinions", which use bearing-supported pins instead of gear teeth to transmit the load, that mesh with linear racks with sprocket-like teeth on them. They claim to achieve zero-backlash by preloading the pinion into the rack so that two rollers are engaged at any one time.
ATLANTA Zero-Backlash Rack & Pinion Drive Systems utilize a split-pinion, which consists of two pinion halves and an axial spring pack, to remove the system backlash. The pinions halves mesh with opposite tooth flanks on the same rack, eliminating the backlash. One pinion half drives the axis while the second pinion half is "preloaded" to remove the backlash.
Below is a comparison showing how ATLANTA Zero-Backlash Rack & Pinion Drives stand up against them.
- System Overview
- System Preloading
- System Size
- Conclusion
| Roller-Pinion System | ATLANTA Zero-Backlash Drive System | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Load Capacity | Pinion Pitch Diameter | ATLANTA Solution | Load Capacity | Pinion Pitch Diameter |
| RPS10 | 250 N | 31.8 mm | Module 2.0 Rack & Split-Pinion | 2,800 N | 63.66 mm |
| RPS12 | 500 N | 38.2 mm | |||
| RPS16 | 1,000 N | 50.9 mm | |||
| RPS20 | 1,500 N | 63.7 mm | |||
| RPS25 | 2,200 N | 79.6 mm | |||
| RPS32 | 3,600 N | 122.2 mm | Module 3.0 Rack & Split-Pinion | 5,200 N | |
| RPS40 | 6,000 N | 152.8 mm | Module 4.0 Rack & Split-Pinion | 8,000 N | |
| RPS4014 | 14,000 N | 178.3 mm | Module 6.0 Rack & Split-Pinion | 15,600 N | 82.76 mm |
| RPS50 | 19,000 N | 191.0 mm | Module 8.0 Rack & Split-Pinion | 27,500 N | 101.86 mm |
Lifetime: It should be noted that the Roller-Pinion System ratings are based on a limited lifetime of between 2 and 30 million cycles, depending on the version used. All ATLANTA rack & pinion drives are selected to achieve a minimum lifetime of 100 million cycles.
In order to ensure zero-backlash, the Roller-Pinion System requires that the pinion is always preloaded into the rack. This preload must be accurately controlled and maintained for the full travel length. If excessive preload is applied, the product lifetime will be decreased and increased noise and vibration could be seen. If the preload is removed, backlash will be present. This means that if the rack is not accurately mounted to within +/- 0.001" over the full travel length, the preload will vary greatly and the system performance will not be consistent.
While the ATLANTA Zero-Backlash Split-Pinions also require accurate rack mounting and alignment, the split-pinion can accept a much larger variation than the RPS system. Because the preload setting of the split-pinion is set depending on the application running parameters, it can take up any rack misalignment that exists and ensures that NO backlash develops along the full travel length.
In the below graphics, the relative drive sizes and load capacities are shown for comparably rated roller-pinion and rack and pinion drive systems.
RPS16: 1,000 N Thrust Capacity, 11.5 mm Rack Face Width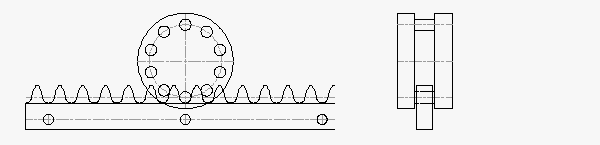
RPS20: 1,500 N Thrust Capacity, 15.5 mm Rack Face Width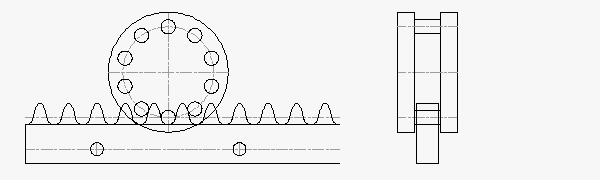
RPS25: 2,200 N Thrust Capacity, 18.5 mm Rack Face Width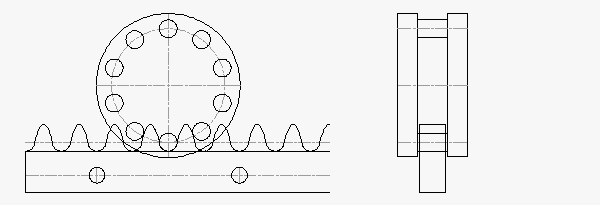
The first three sizes of the roller-pinion systems have capacities up to 2,200 N (494 lb.). The ATLANTA module 2.0 helical hardened & ground rack and zero-backlash split-pinion drive system is rated for 2,800 N (629 lb) of thrust. The split-pinion pitch diameter is 63.66 mm, compared to 50.9 mm, 63.7 mm and 79.6 mm for the first three sizes of the RPS.
ATLANTA Module 2.0 Rack & Split-Pinion: 2,800 N Thrust Capacity, 24 mm Rack Face Width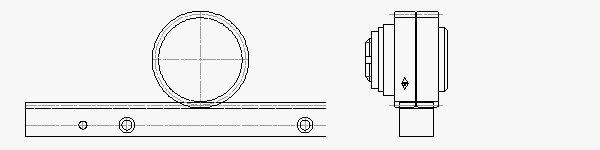
As you can see, the module 2.0 rack & pinion system is dimensionally smaller than the first three sizes of the RPS system, but is rated higher.
RPS32: 3,600 N Thrust Capacity, 24.5 mm Rack Face Width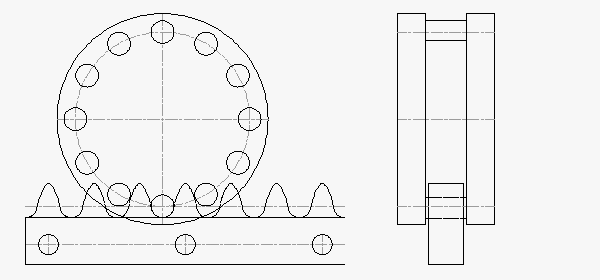
As the roller-pinion systems get progressively larger, the packaging differences become more apparent. The RPS32 is rated for 3,600 N (809 lb) with a 122.2 mm pinion diameter.
The ATLANTA module 3.0 helical hardened & ground rack and zero-backlash split-pinion drive system is rated for 5,200 N (1,169 lb) of thrust in a much smaller package. The split-pinion pitch diameter remains at 63.66 mm, almost half the size of the RPS.
ATLANTA Module 3.0 Rack & Split-Pinion: 5,200 N Thrust Capacity, 29 mm Rack Face Width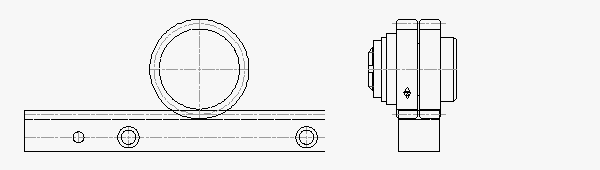
RPS40: 6,000 N Thrust Capacity, 31.5 mm Rack Face Width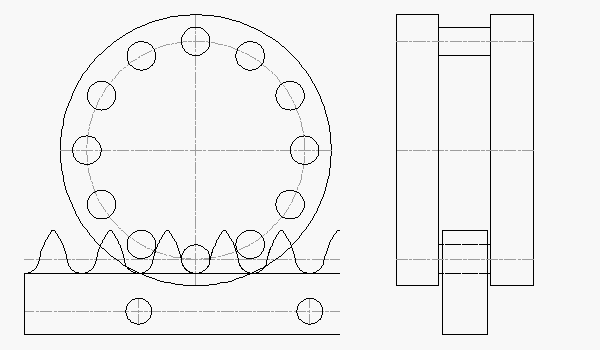
The roller-pinion systems continue to grow larger dimensionally with only slight improvements in the load capacity. The RPS40 is rated for 6,000 N (1,348 lb) with a 152.8 mm pinion diameter.
The ATLANTA module 4.0 helical hardened & ground rack and zero-backlash split-pinion drive system is rated for 8,000 N (1,798 lb) of thrust in a much smaller package. The split-pinion pitch diameter remains at 63.66 mm, less than half the size of the RPS.
ATLANTA Module 4.0 Rack & Split-Pinion: 8,000 N Thrust Capacity, 39 mm Rack Face Width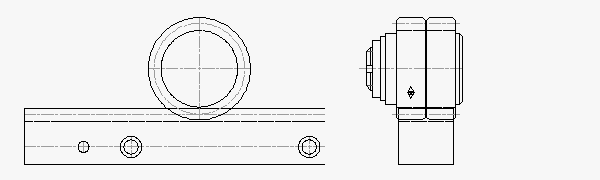
RPS4014: 14,000 N Thrust Capacity, 42 mm Rack Face Width
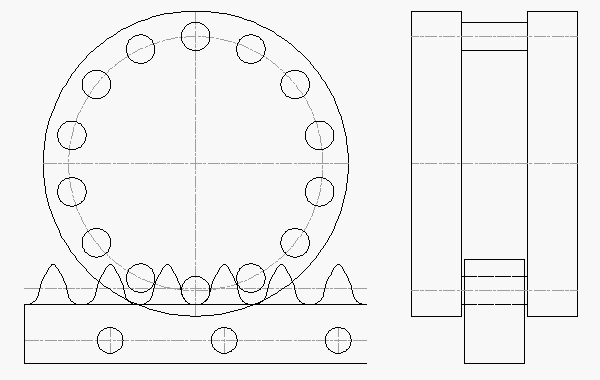
The RPS4014 has a rating of 14,000 N (3,147 lb) with a 178.3 mm pinion diameter.
The ATLANTA module 6.0 helical hardened & ground rack and zero-backlash split-pinion drive system is rated for 15,600 N (3,507 lb) of thrust in a much smaller package. The split-pinion pitch diameter is 82.76 mm, less than half the size of the RPS.
Module 6.0 Rack & Split-Pinion: 15,600 N Thrust Capacity, 59 mm Rack Face Width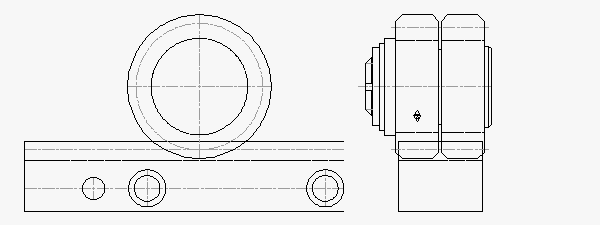
RPS50: 19,000 N Thrust Capacity, 42 mm Rack Face Width
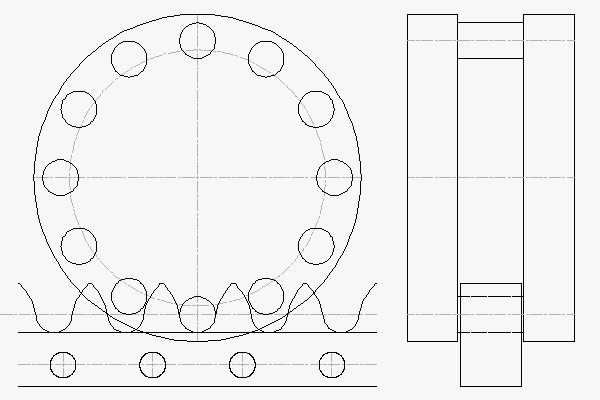
The largest roller-pinion system RPS50 tops out at 19,000 N (4,271 lb) with a 191.0 mm pinion diameter.
The ATLANTA module 8.0 helical hardened & ground rack and zero-backlash split-pinion drive system is rated for 27,500 N (6,182 lb) of thrust in a much smaller package. The split-pinion pitch diameter is 101.86 mm, almost half the size of the RPS.
Module 8.0 Rack & Split-Pinion: 27,500 N Thrust Capacity, 79 mm Rack Face Width
Electrical preloaded drive systems, which use two motor/reducer assemblies with dual pinions operating on the same rack to remove the backlash, are also available in force capacities up to 124,000 N (28,000 lb).
In the previous graphics, it can be seen that the ATLANTA Zero-Backlash Drive Systems have a much higher power density than the roller-pinion systems. On most comparable systems by load, the ATLANTA system is half the size of the roller-pinion system. The roller-pinion system pinion diameters are very large because they must have three pins engaged at all times.
Advantages of Using Small Pinions: The pinion diameter has a huge effect on the system, including the gearbox torque, size, ratio, linear backlash, linear stiffness and resonant frequency of the system. ATLANTA has a wide range of pinions, including ISO flanged pinions, which gives the design engineer flexibility to optimize his design.
The accurate preload required by the roller-pinion system becomes very difficult to achieve over a long travel length and if the preload is too high or too low, problems will result. ATLANTA Zero-Backlash Drive Systems are much more flexible with the rack alignment and preload setting, and will maintain zero-backlash even if there is some misalignment.
Advantages of ATLANTA Zero-Backlash Rack & Pinion Drive Systems:
- Extremely high power density (load capacity per space required)
- Flexible alignment and preload requirements
- Small pinion pitch diameter reduces required torque & gearbox size, improves system dynamics
- Racks available in two meter lengths for reduced assembly time
- Lower price than roller-pinion systems
- All ATLANTA rack & pinion drives are selected to achieve a minimum lifetime of 100 million cycles.
Disadvantages of Roller-Pinion Systems (RPS):
- Low power density (load capacity per space required)
- Rigid alignment and preload requirements
- Large pinion pitch diameter increases required torque & gearbox size
- Racks only available in lengths up to one meter long
- Higher price than traditional rack & pinion drives
- Roller-Pinion System ratings are based on a limited lifetime of between 2 and 30 million cycles, depending on the version used.